Composite
The Composite Group at the Knowledge-Based Company Carbon Polymer Ghadir offers independent services in engineering for continuous fiber-reinforced polymers and particulate composites. The main goal of this company is to increase production rates and product quality through the use of up-to-date composite forming processes. Our experienced team has been providing independent composite engineering services to designers and manufacturers since the 2010s. These services include:
- Process design tailored to the product
- Analysis, design, and optimization of lay-up
- Extraction of technical knowledge for specific products
- Analysis and standardization of products
- Pre-production study
- Design and construction of molds
- Development of simplified processes
- Feasibility studies for complex productions
- Production coaching
Services:
At Carbon Polymer Ghadir Company, we help you achieve your goals based on the type of product, required production rate, time, and cost by relying on the technical knowledge of our specialist team and utilizing the following processes. Composite forming processes can be categorized based on the type of mold as follows:
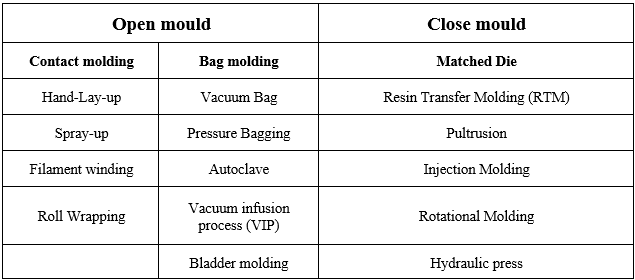
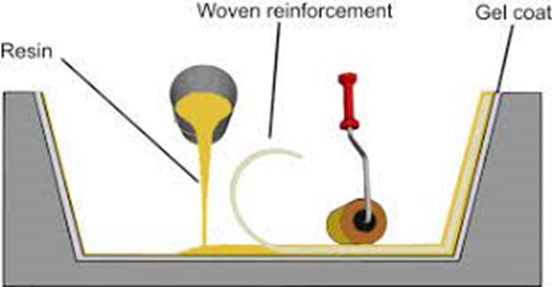
Hand-Lay-up Method
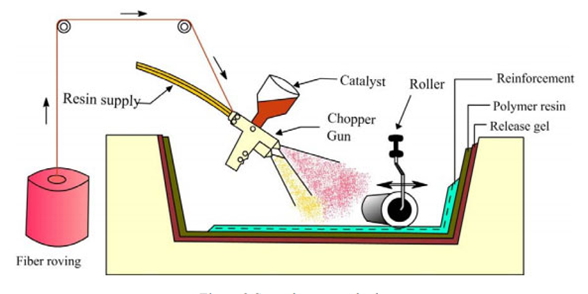
Spray-up
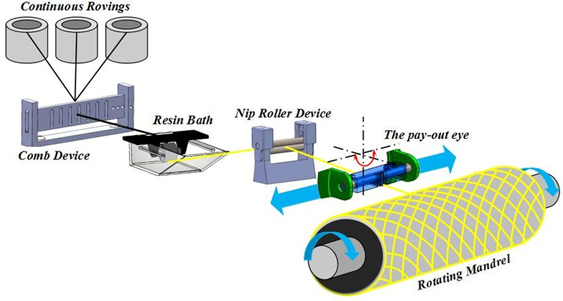
Filament Winding
Introduction: Filament winding is a process in which continuous strands or tapes of various materials such as glass fibers, carbon fibers, or aramid are regularly and pre-arranged, wound around a rotating mandrel after being impregnated with resin, and then cured. Once the resin hardens, the mandrel is removed, resulting in a final product that is a high-strength hollow structure. Filament winding is commonly used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, marine, and energy for producing lightweight, high-strength, and corrosion-resistant parts such as pressure vessels, rocket motor casings, pipes, and structural composites.
Vacuum Bag Molding
Introduction: Vacuum bagging is a widely used technique in composite manufacturing for creating high-quality, lightweight parts with excellent surface finish and suitable mechanical properties. This method involves applying vacuum pressure to a composite layer, consisting of reinforcing materials and resin, inside a sealed bag to remove trapped air and excess resin. The vacuum bagging process can be performed in two different ways: 1- Hand lay-up vacuum bagging, where the composite is impregnated manually using ambient curing resins, and 2- Only vacuum bag prepreg cure, where the pre-impregnated composite is cured at high temperature in a vacuum bag. Vacuum bagging is commonly used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, marine, and wind energy to produce a wide range of composite components.
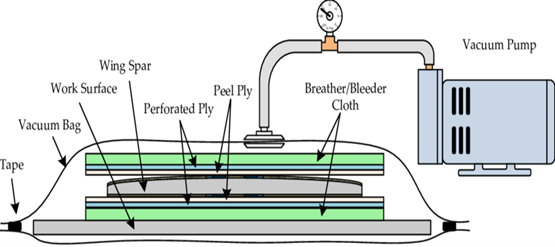
Autoclave
Introduction: The autoclave method is a widely used technique in composite manufacturing for producing high-quality and high-performance parts with excellent mechanical properties and surface finish. This method involves subjecting composite materials to high temperature and pressure inside an autoclave chamber. Autoclave processing is commonly used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, marine, and sports goods for manufacturing components like aircraft structures, automotive body panels, boat hulls, and sports equipment.

Vacuum Infusion Process (VIP)
Introduction: The Vacuum Infusion Process (VIP) is a popular and versatile technique in composite manufacturing used to produce high-quality, large-scale composite parts with excellent mechanical properties and surface finish. This method involves the infusion of resin into a dry fiber reinforcement layer under vacuum, ensuring complete resin saturation and uniform compaction. Despite some limitations, vacuum infusion offers numerous advantages such as reduced void content, design flexibility, environmental compatibility, and cost efficiency, making it an essential choice for industries requiring lightweight, high-strength, and structurally efficient composite materials.

Bladder Molding
Introduction: Bladder molding is a specialized technique in composite manufacturing used to produce hollow or complex-shaped composite parts with intricate internal features. This method involves using a bladder or inflatable punch to apply pressure from inside a layer of composite materials, which facilitates the stabilization of the part and ensures uniform compaction and resin distribution. Bladder molding is commonly used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, marine equipment manufacturing, and sports equipment for producing components like aircraft fuselages, automotive fuel tanks, boat hulls, and bicycle frames.

Roll Wrapping Process
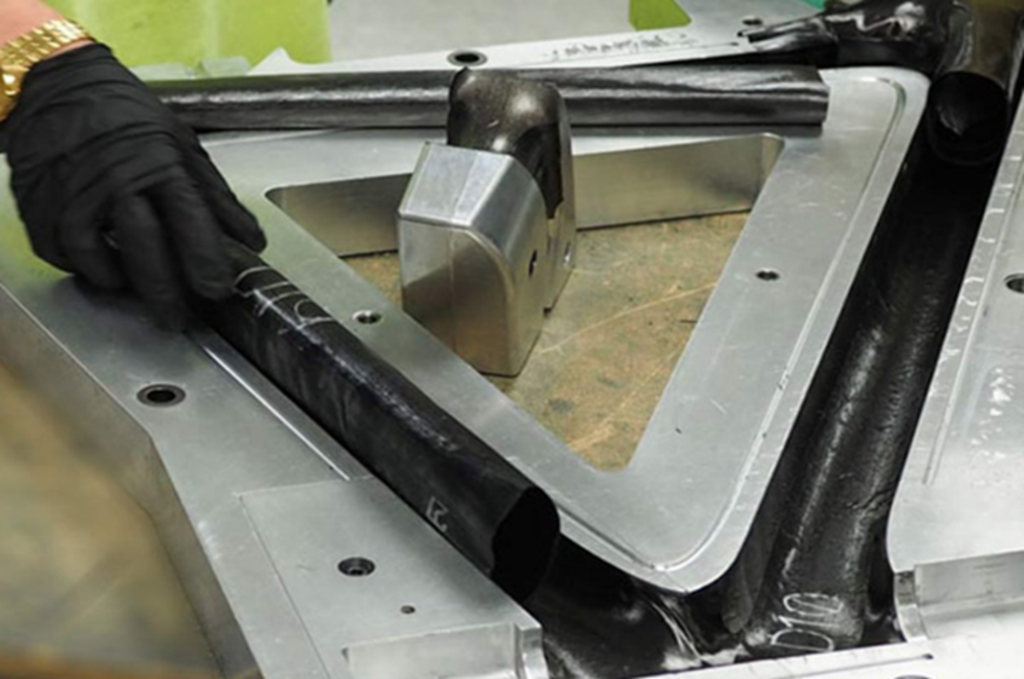
Introduction: Ultra-light composite tubes are structures created by wrapping pre-impregnated composite fabrics—such as carbon fibers or glass fibers—around a mandrel. The fabric layers are typically oriented in different directions to optimize strength and stiffness. In this process, the mechanical properties of the tube are adjusted by aligning the fibers in each layer in various directions, such as axial, hoop, and ±45 degrees. This unique flexibility allows for the optimization of strength, stiffness, and other performance characteristics. To apply pressure and ensure layer impregnation, the wrapped fabrics are covered with shrinkable plastics. In the final stage, the tube is cured in a thermal oven, resulting in a lightweight and strong cylindrical structure.

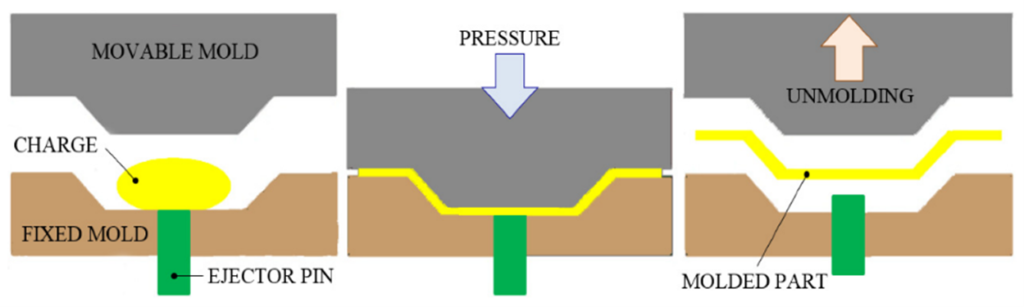
Pressure Molding
Introduction: The Matched Die method, also known as closed molding or compression molding, is a widely used technique in composite manufacturing for producing high-quality parts with precise dimensions and consistent mechanical properties. This method involves using closed metal molds to shape and consolidate dry fiber reinforcement materials impregnated with resin. The Matched Die method is commonly used in industries such as automotive and sports goods for producing components like automotive body panels and sports equipment.
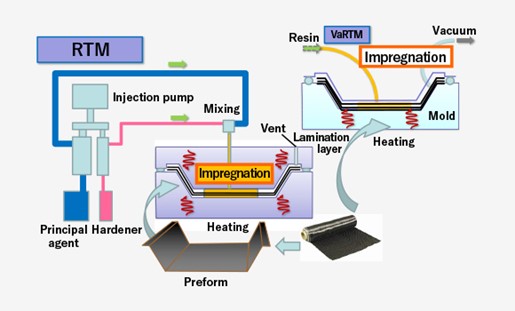
Resin Transfer Molding (RTM)
Introduction: Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) is a closed-mold composite manufacturing process used to produce parts with complex shapes, high quality, and repeatable mechanical properties. This method involves injecting resin into a pre-formed dry fiber reinforcement within a closed mold under pressure, allowing for effective saturation and precise control of the resin-to-fiber ratio. RTM is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, marine, and wind energy to produce lightweight and durable composite components.
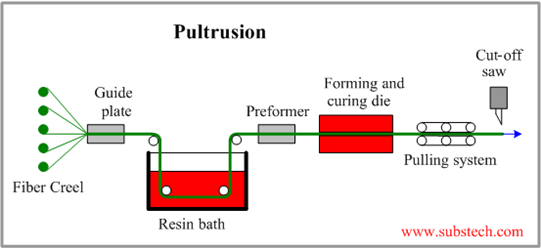
Pultrusion
Introduction: Pultrusion is a continuous manufacturing process used to produce composite profiles with constant cross-sectional shapes, such as rods, tubes, channels, and angles. This method is widely used in various industries due to its efficiency in producing composite materials that are high-strength, lightweight, and resistant to corrosion. Pultrusion involves pulling reinforcing fibers through a resin bath, followed by a shaping die and a heated die, to form a cured composite profile with desirable mechanical properties.
High-Pressure Resin Transfer Molding (HP-RTM)
Introduction: High-Pressure Resin Transfer Molding (HP-RTM) is an advanced method for composite part manufacturing that combines the benefits of both resin injection and compression molding techniques. In this process, thermosetting resin is injected directly into a closed mold and then subjected to high pressure to ensure complete penetration between the reinforcing fibers. After curing, this process results in the formation of the final composite part.
